4 - Creating Variables
This is class #04 of Interactive Beginners Guide to MATLAB. In this video I will tell you how you can create variables in MATLAB.
You can create new variables in the workspace by running MATLAB code or using existing variables.
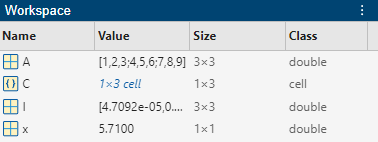
To create a new variable, enter the variable name in the Command Window, followed by an equal sign (=) and the value you want to assign to the variable. For example, if you run these statements, MATLAB adds the three variables x, A, and I to the workspace:
You do not have to declare variables before assigning values to them.
If you do not end the assignment statement with a semicolon (;), MATLAB displays the result in the Command Window. For example,
If you do not explicitly assign the output of a statement to a variable, MATLAB generally assigns the result to the reserved word ans. The value of ans changes with every statement that returns an output value that is not assigned to a variable. For example,
sin(1)
ans =
0.8415
[post_ad]
You can create new variables in the workspace by running MATLAB code or using existing variables.
To create a new variable, enter the variable name in the Command Window, followed by an equal sign (=) and the value you want to assign to the variable. For example, if you run these statements, MATLAB adds the three variables x, A, and I to the workspace:
x = 5.71;
A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9];
I = besseli(x,A);

You do not have to declare variables before assigning values to them.
If you do not end the assignment statement with a semicolon (;), MATLAB displays the result in the Command Window. For example,
x = 5.71
x =
5.7100
If you do not explicitly assign the output of a statement to a variable, MATLAB generally assigns the result to the reserved word ans. The value of ans changes with every statement that returns an output value that is not assigned to a variable. For example,
sin(1)
ans =
0.8415
[post_ad]
4 - Creating Variables
 Reviewed by Usman Ibrahim
on
04:37
Rating:
Reviewed by Usman Ibrahim
on
04:37
Rating:
 Reviewed by Usman Ibrahim
on
04:37
Rating:
Reviewed by Usman Ibrahim
on
04:37
Rating:








No comments: